Some text
The 14th Conference of the International Society for Priorities in Health (ISPH) – Priorities Conference 2024 –, an international forum for healthcare priority setting, took place in Bangkok from May 8th to 10th. The conference was hosted by the Health Intervention and Technology Assessment Program (HITAP), the Ministry of Public Health – Thailand, and the International Society for Priorities in Health (ISPH). This year’s theme, “Shaping the Future of Health Prioritization: Strategies for Sustainable Solutions”, drew academics, researchers, policymakers, health professionals, and other interested groups from around the globe to engage in knowledge exchange, foster collaborations, enhance professional development, and explore innovative strategies for Universal Health Coverage (UHC) and the attainment of the 2030 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
A highlight of the conference was a presentation by Demelash Assefa, member of our team and representative of KNCV Tuberculosis Foundation, who showcased the organization’s work on evidence-based tuberculosis (TB) planning in resource constrained settings. The presentation titled “Evidence-Based TB Planning in Resource-Limited Countries: Experience on Intervention Prioritization Processes in Ethiopia and Namibia”, outlined a comprehensive approach to optimizing TB interventions using the Tuberculosis Intervention Measure and Estimate (TIME) model.
While presenting, Demelash underscored the relevance of scenario-based modeling to identify the most efficient interventions for resource allocation. the study highlighter that a combination of interventions, rather than a single strategy, is essential to achieve substantial progress towards the common goal to ending TB.

Demelash has been a key player in the intervention modeling, scenario optimization and costing explored with the PCF4TB project.
Key findings in this presentation included:
- In Namibia, the most comprehensive intervention scenario, which combined molecular testing expansion, active TB case finding, and the introduction of TB preventive treatment for high-risk groups, projected a 54% decline in TB incidence and a 55% reduction in mortality by the end of the National Strategic Planning period.
- In Ethiopia, the same comprehensive approach was projected to result in a 41% decline in TB incidence and a 50% reduction in mortality.
The presentation emphasized the importance of the People-Centred Framework (PCF) for NSP, advocating for a tailored approach to TB interventions that consider the unique contexts and needs of each country at a national and subnational levels. Sharing knowledge and experiences from these findings has contributed valuable insights for policymakers and health professionals striving to enhance local and global efforts to end TB, with special emphasis on resource limited settings.
For more information about the Priorities Conference 2024, visit their website HERE.
The People-Centred Framework for TB programming was jointly developed by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, The Royal Tropical Institute Netherlands (KIT), the World Health Organization, Linksbridge, TB Modeling and Analysis Consortium, and refined by KNCV Tuberculosis Foundation.The goal of the initiative is provide countries with the necessary tools and approaches to optimize their National Strategic Plans in line with the End TB Strategy, Sustainable Development Goals and country commitments. The goal of the initiative is provide countries with the necessary tools and approaches to optimize their National Strategic Plans in line with the End TB Strategy, Sustainable Development Goals and country commitments. The framework is a process for country-level planning with four primary planning steps centered on answering the questions in the figure below (right click the image to view a larger size in a new tab):
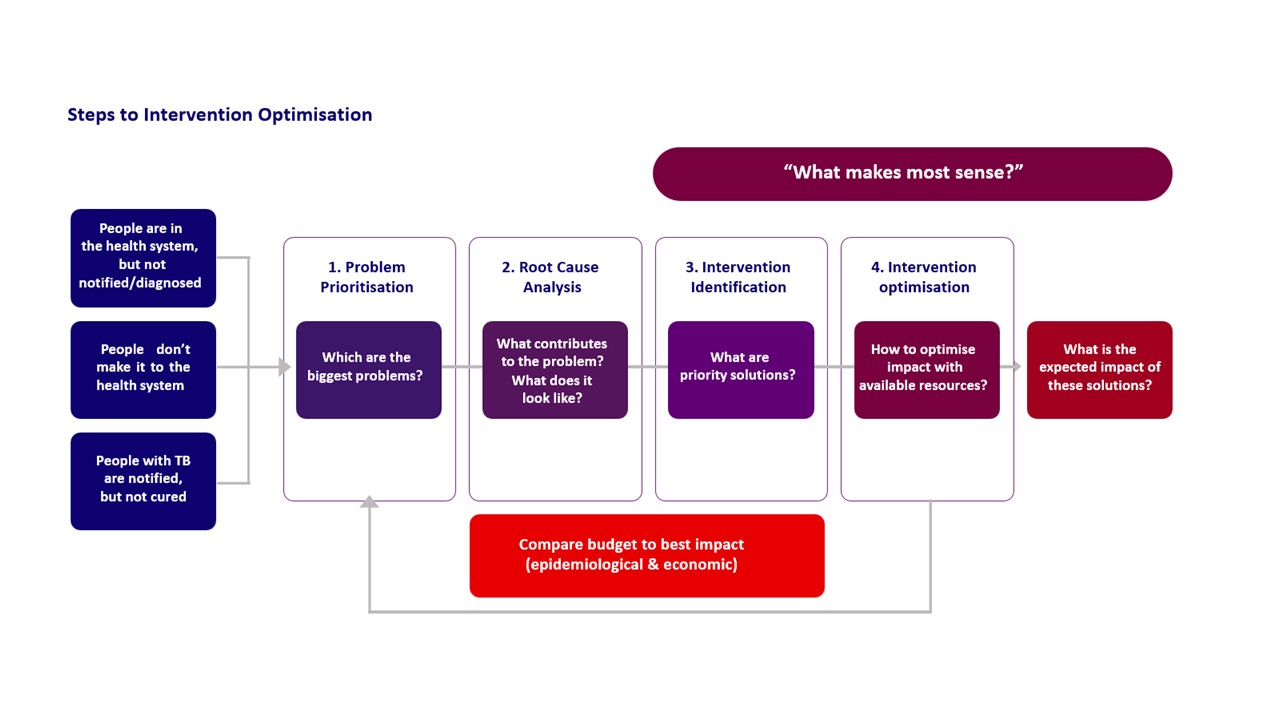 The framework is a process for country-level planning with four primary planning steps centered on answering the questions in the figure below:
The framework is a process for country-level planning with four primary planning steps centered on answering the questions in the figure below:
